KLV
Introduction
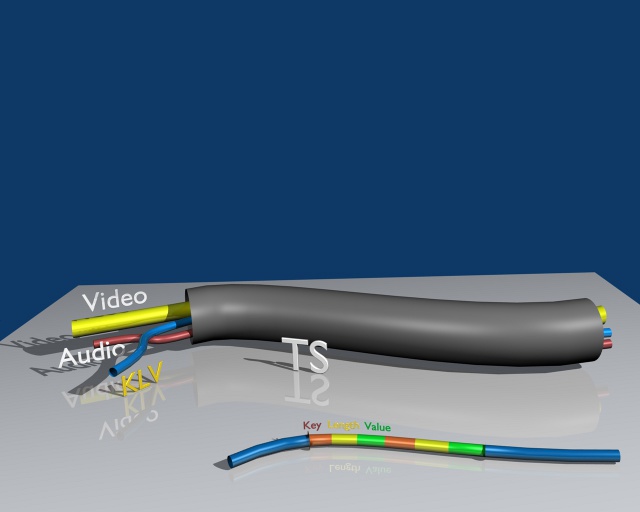
KLV (Key-Length-Value) is a data encoding standard used for binary data byte-packing and metadata embedding into video feeds. Data is encoded into Key-Length-Value triplets, where Key identifies the data, Length specifies the data's length, and Value is the data itself. It is defined in SMPTE 336M-2007 (Data Encoding Protocol Using Key-Length Value), approved by the Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers. KLV encoding protocol defines a data structure which is independent of the application or transportation method used.
MISBCore SDK has a KLV encoder / decoder library integrated, so for generic STANAG 4609 metadata related tasks there is no need to deal with it explicitly - user either provides KLV encoded data buffer (at the client side) and gets the decoded metadata back or (at the server/encoder side) supplies the structured (as json) metadata and receives a KLV encoded data buffer.
Encoding/decoding metadata for Unmanned Air System (UAS)
Unmanned Air Systems use two types of KLV encoded metadata. Universal Data Set (UDS) - the 16-byte key, basic encoding rules (BER) formatted length, and data value is appropriate for applications where bandwidth isn't a concern. However, transmitting the 16-byte universal key quickly uses up the available bandwidth. UAS airborne platforms use a wireless communications channel where the bandwidth allocated for metadata is limited. Because of the bandwidth disadvantages of using a Universal Data Set, it is more desirable to use a Local Data Set for transmission over a UAS Datalink. Local Data Set can use a 1, 2 or 4-byte key with a 1, 2, 4-byte, or BER encoded length. For more info about KLV use in UAS application see KLV in UAS applications
[1] SMPTE ST 336:2017 Data Encoding Protocol Using Key-Length-Value.
[2] MISB MISP-2019.1: Motion Imagery Handbook, Nov 2018.